The recent warming trend in global temperatures D. Which of the following is a glacial deposit and not a glacial erosional feature.
16 3 Glacial Erosion Physical Geology
Eskers are usually several kilometers long.
. Corn sugarcane amaranth mostly grasses but some shrubs too which are cold tolerant. C a cirque glacier. Furthermore what are some examples of glacial erosion.
Alpine vegetation is found at places over 3600 m in height. A fiord is _____. An alpine tundra is a biome that does not contain trees because of the high elevation.
Examples for C 4. Correct option is D Examples of C 3. Identify features in a glacial system.
The continental glaciers in Greenland C. The trees get stunted as they reach the snow line. Due to their peculiar shape these landforms are often compared to railway embankments.
Thus it does not lie completely in the temperate alpine zone. The strong tendency of certain minerals to break along smooth parallel planes is known as _____. The biome exhibit cold environmental conditions and rock bearing land.
Which of the following adaptations is characteristic of animals in the alpine biome. The polar ice caps are a permanent feature on Earth. Ice cores that show the climate was once warmer.
Which of the following suggests that Earth is currently in an ice age. The Alpine forests are found all along the Himalaya at altitude ranging between 2500 m to 3500 m. A tarn is a lake in a.
Alpine glaciers are smaller compared to the continental glaciers. One of the most notable examples is a large trough right down the middle of the country that was created by a glacier moving slowly over it. Solve any question of.
29 Alpine glaciers include all of the following except. It exists as a long narrow ridge that winds along a glacial valley or canyon. An earthquake a submarine landslide or an eruption of an undersea volcano is capable of producing a wave in the open ocean of great height.
A long-lasting body of ice on land that moves under its own weight. Basalt is the fine-grained equivalent of gabbro. Steep peaks that have been glacially and freeze-thaw eroded on three or more sides.
While alpines are found only in mountaintops continental glaciers can be found in earths poles regardless of its elevation. A pyramidal peak caused by several cirque glaciers gouging a mountain on all sides mountain tarn. Streak cleavage cracking luster crystal form.
Piedmont glaciers form on lowlands at the base of mountainous terrain. The smallest features shaped by individual saltating grains are reg deserts. The following features are commonly created by alpine glaciers.
Zone of accumulation glacier terminus e base of glacier glacialice Which of the following is a type of mountain alpine glacier. It is occupied by are succulent plants storing water in their leaves waxy leaves that prevent desiccation and mosses. 30 A glacier that is confined in a bowl-shaped recess is called a.
Which of the following basin and range features would you not find in a basin. With brief exceptions there have. Glassy igneous rocks form when magma cools too fast for.
The trees common to these are silver fir junipers pines and birches. A scooped out basin at the head of an alpine glacier mountain arete. A glacier that covers a significant part of a continent and has an area of at least 50000 km2.
Bowl-shaped basins that form at the head of a glacial valley. 100 24 ratings Transcribed image text. End moraine medial moraine ground moraines eskers.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Low points along arêtes that constitute passes between glacial valleys. An open fissure on the surface of a glacier.
A an ice cap. Both of the glaciers move and are. There are shrubs and scrubs that ultimately merge into Alpine grasslands.
Large streamlined hills of till and bedrock that form in come areas subjected to continental glaciation are called. Valley of Flowers National Park - At 3352 to 3658 meters above sea level. Horns and cirques are typical features in.
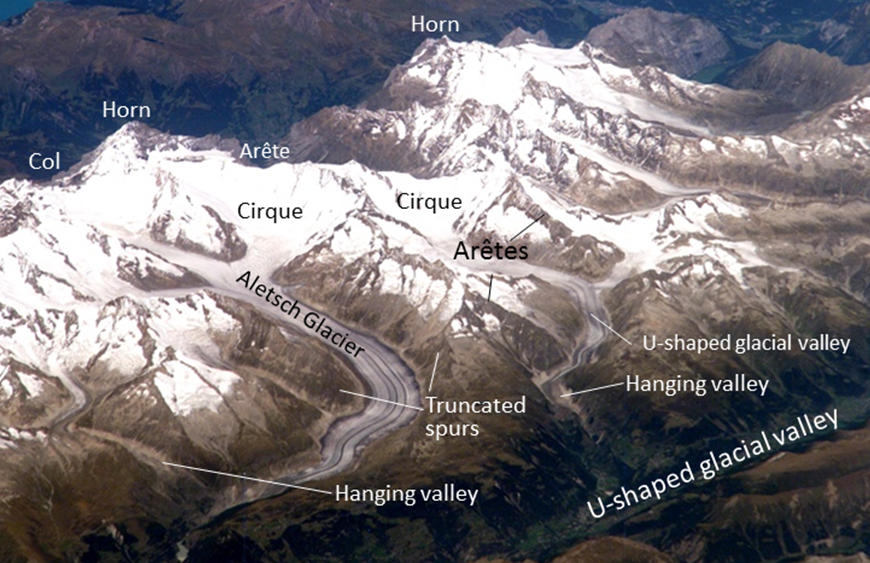
Some of the important features visible in Figure 1622 are arêtes. A glacier formed in a mountainous region and confined to a valley. Beans rice wheat potatoes most temperate crops and all woody trees.
They are made up of layers of gravel and sand. Pass or saddle-like depression along an arete caused by erosion mountain horn. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Horn arête cirque moraine and hanging valley. B a mountain glacier. A cirque a moraine an arete a horn.
Alpine glaciers are found in the mountain tops but continental glaciers are found in masses like Greenland. Namdapha National Park has a very wide altitude variation from 200 m to 4500 m in the snow-capped mountain. Which of the following is not an erosional feature formed by an alpine glacier.
The alpine glaciers in Switzerland B. Sharp ridges between U-shaped glacial valleys. Long extended alpine glaciers occupied valleys in most high mountainous areas in the United States Canada and Europe at one or more times during the past two million years.
A a stream valley deepened by glacial erosion that floods as sea level rises B a glacier-cut valley that is dammed by an end moraine and a large lake is formed C a glacier-cut valley which sinks below sea level due to glacial rebound after the ice melts D a large kettle-pocked moraine left as an island when sea level rises following melting of the ice. Alpine glaciers include all of the following except an A cirque glacier. A mountain range that was sculpted by alpine glaciers.
D a valley glacier. An esker is also a depositional landform formed by glacial action. A sharp ridge that divides 2 cirque basins mountain col.
Which feature forms where two lateral moraines merge.
16 3 Glacial Erosion Physical Geology

The Seasonal Alpine Mixed Collection 1l Pot X 6 Small Rock Garden Ideas Rock Garden Rock Garden Design
0 Comments